Vitiligo
1. Signs and Symptoms of Vitiligo
- Patchy Skin Discoloration: Characterized by white, chalky patches on the skin.
- Premature Hair Whitening: Hair in affected areas may turn white or gray.
- Color Loss on Mucous Membranes: Discoloration can occur inside the mouth or nose.
- Retinal Pigment Changes: Rarely, the retina at the back of the eye may lose color.
- No Physical Discomfort: Typically, there is no itching or pain associated with the patches.
2. Causes of Vitiligo
- Autoimmune Disorder: The immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys melanocytes.
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of vitiligo increases the risk.
- Neurogenic Factors: Nerve endings in the skin may release chemicals toxic to melanocytes.
- Oxidative Stress: An imbalance of free radicals and antioxidants can damage cells.
- Environmental Triggers: Exposure to certain chemicals or severe sunburns may initiate vitiligo
3. Different Types of Vitiligo
- Non-Segmental Vitiligo (Generalized Vitiligo): This is the most common type, with patches appearing symmetrically on both sides of the body. It often spreads over time and can affect various body parts.
- Segmental Vitiligo: Affects only one side or segment of the body. It typically starts at a younger age, spreads for a limited period, and then stabilizes. It’s often associated with nerve pathways.
4. Other Types of Vitiligo
- Focal Vitiligo: Characterized by one or a few localized patches in a small area.
- Acrofacial Vitiligo: Primarily affects the fingers, toes, and areas around body openings like the mouth, eyes, and nostrils.
- Universal Vitiligo: A rare and extensive form where most of the body (80% or more) loses its pigment.
5. Differential Diagnosis
Differentiating Vitiligo from conditions like Tinea versicolor, Pityriasis alba, chemical leukoderma, and post-inflammatory hypopigmentation is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
6. Prevention of Vitiligo
While complete prevention is challenging due to its autoimmune nature, managing stress, protecting skin from excessive sun exposure, and avoiding harsh chemicals can help potentially reduce triggers and progression.
7. Diet Restrictions for Vitiligo
- Avoid: Citrus fruits (especially sour ones), red meat, excessive junk food, and highly processed foods.
- Limit: Dairy products, fermented foods, and nightshades (tomatoes, potatoes, bell peppers).
- Add: Antioxidant-rich foods like leafy greens, berries, turmeric, and ginger. Include foods rich in Vitamin B12 and Folic Acid.
8. Homeopathic Treatment for Vitiligo
Homeopathy offers a holistic approach to Vitiligo by addressing the root cause and stimulating the body’s natural healing mechanisms. Our individualized treatments aim to:
- Stimulate Melanocyte Production: Promote the regeneration of pigment-producing cells.
- Modulate Immune Response: Help balance the immune system to stop attacks on melanocytes.
- Reduce Stress and Anxiety: Address emotional factors that can exacerbate the condition.
- Improve Overall Health: Enhance general well-being, leading to better skin health.
- Minimize Recurrence: Strengthen the body’s resilience against future depigmentation.
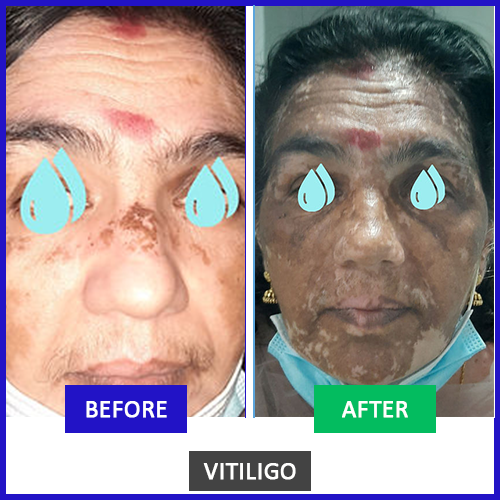
9. Success Stories
(Imagine an image of a person proudly displaying their repigmented skin, perhaps a before-and-after, or just a happy individual.)
“Witness the incredible journeys of our patients who have found renewed hope and regained their natural skin tone through our personalized homeopathic care. This inspiring transformation is a testament to the power of holistic healing and the dedication of our expert team at CureYou. We celebrate each step towards confidence and vibrant health!”
Any questions? We're here to help
What is Vitiligo?
Vitiligo is a chronic skin condition where patches of skin lose their natural color. This occurs when melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing pigment, are destroyed. It can affect any part of the body, including hair and the inside of the mouth.

